This is paragraph text. Click it or hit the Manage Text button to change the font, color, size, format, and more. To set up site-wide paragraph and title styles, go to Site Theme.
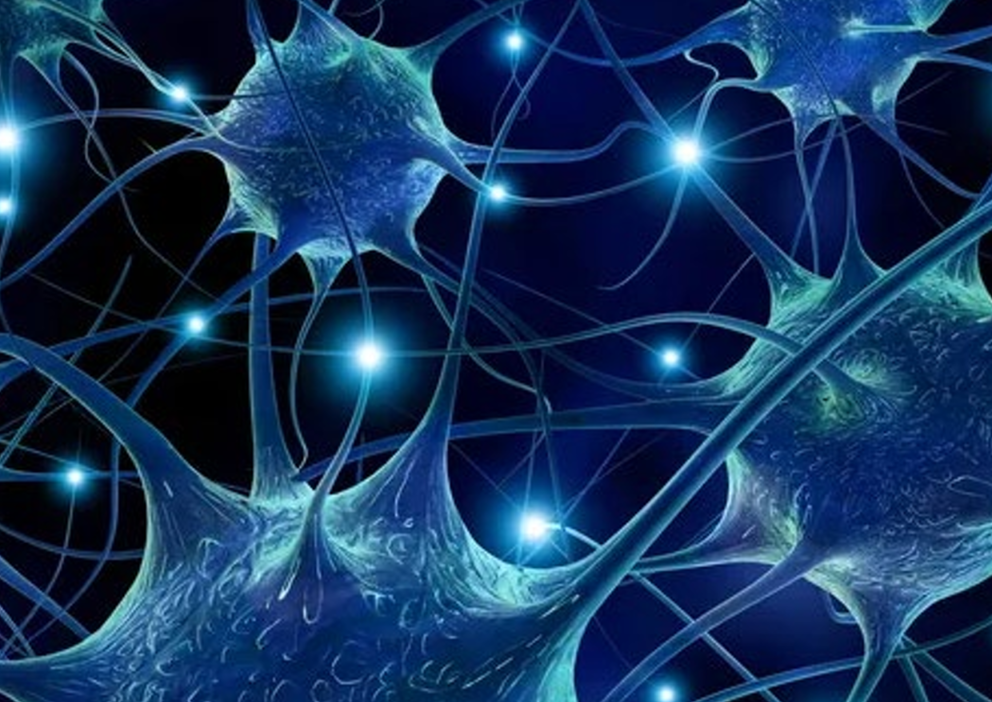

A major brain injury can result in the loss of brain tissue, the disruption of connections among regions of the nervous system, the destruction of specific brain regions that control various functions or sensations, and the creation of chaotic electrical activity that disrupts other brain signaling.
To maximize healing in the damaged brain, minimizing the impact of the initial injury in the early hours and days after the trauma is essential. Bleeding and swelling must be controlled. Ongoing damage and scarring of the brain as a result of inflammation and disruption of blood vessels must be limited. Metabolic damage from uncontrolled seizures must be reduced.
Eventually, the storm of the acute events subsides. A person who survives the initial injury enters a future with residual damage and loss of function. Although other tissues and organs are capable of regeneration, human brain tissue does not regrow after damage. Some functional recovery can occur over time, mainly as the person retrains surviving brain regions to take over functions that were served by the injured or disrupted neural tissue. Persons who have survived a severe brain injury usually experience only modest further improvement in the years after their injury.
Recent research has demonstrated that it is plausible to develop medicines and treatments that stimulate the brain to regenerate itself and allow for functional recovery, even years after a devastating injury. The DLF is committed to focusing on developing therapies that will induce brain regeneration and function in persons living in the chronic phase of traumatic brain damage.
Our scientific experts believe that a combination of strategies will be required to allow the brain to experience regrowth and recovery. First, it is necessary to unlock the ability of neurons to grow and replace lost brain tissue. Second, the power of the brain to form new synaptic connections must be enhanced, both in surviving brain regions and in regions repopulated with neurons. Third, the ability of neurons to reconnect to severed axons must be enhanced. Fourth, there must be highly targeted methods to train recovering and regenerating brain regions. Finally, novel devices that connect computers directly to neurons in the brain are being developed. These “brain-computer interfaces” are being designed to re-connect surviving brain regions to allow movement in paralyzed limbs and expression to people who can no longer speak. In each issue of the DLF newsletter, we will highlight one aspect of emerging research about stimulating brain regeneration (see Research Review Corner). We hope that growing awareness of dramatic scientific progress will motivate people to help support this work.
The DLF will focus resources and attention on those scientific projects and initiatives that are most likely to yield medicines that will stimulate brain regeneration and functional recovery. The DLF depends on charitable contributions and grants to fund the research, which will make these possibilities a reality. We hope you find these research updates to be informative and inspiring.