This is paragraph text. Click it or hit the Manage Text button to change the font, color, size, format, and more. To set up site-wide paragraph and title styles, go to Site Theme.
In prior newsletters, we’ve discussed research strategies that bring hope to persons with severe disabilities after a major brain injury. We’ve discussed research focused on creating and transplanting new brain cells to replace damaged tissue [“cellular repletion” ]. We’ve reviewed progress towards stimulating the brain to regrow [“regeneration”] and rewire itself [“axonal repair”] as it seeks to compensate for damage. We’ve explored evidence that the brain can be induced to regenerate new connections [ “synaptogenesis”].
This edition will discuss how biomechanical devices called brain-computer interfaces (“BCIs”) can help a person compensate for an injured brain. We will also explore how new medicines may help a person maximize the benefits of BCIs. The idea of a direct connection between a person’s brain and the external world mediated by a computer sounds like an idea from science fiction. Nevertheless, brain-computer interface devices have been developed and are beginning to be implanted in patients.
What is a BCI?
At its essence, a brain-computer interface is a system that allows direct communication between the human brain and the world, either for sensory inputs or motor outputs. Imagine typing a message, playing a song, controlling an artificial limb, or steering a wheelchair merely by thinking about it. Picture a blind person having a camera-like device that is hardwired to the visual cortex to enable sight or a glove that transmits sensory information directly to the cortex for interpretation. More formally, a BCI is a type of prosthesis that allows regions of the brain to be reconnected to parts of the body or the outside world after the natural neuronal connections have been lost. BCIs connect the world to the brain for interpretation and the brain to the world for action.
How Do BCIs Work?
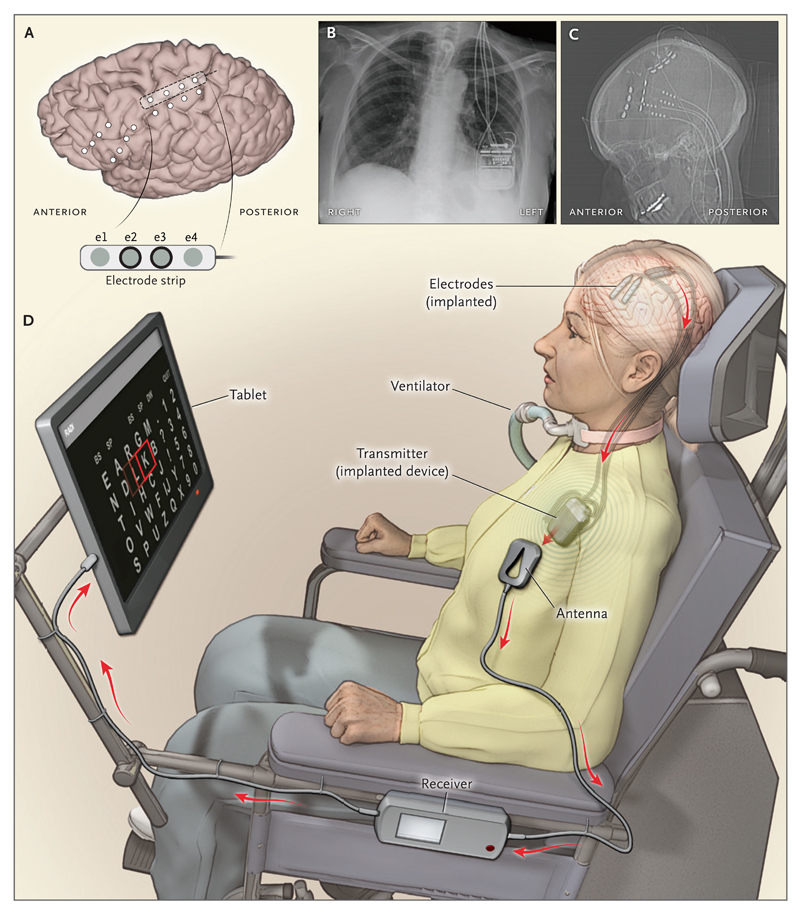
The magic behind BCIs lies in their ability to decode and encode the brain's electrical signals. Our thoughts and intentions spark neural activity, generating distinctive electrical patterns. Our sensations exist as patterns of neuronal excitation in the brain. BCIs can control limbs or external devices by detecting the electrical patterns of intentions and then translating these signals into commands that can control a prosthetic limb, a cursor on a screen, or the hand of a person whose spinal cord has been severed. BCIs tap into the brain’s electrical activity using various sensors placed on the scalp (non-invasively) or directly within the brain (invasively) to detect and record these signals. Once these signals are captured, they are fed into a computer that interprets them using sophisticated algorithms. This process translates the brain's electrical activity into commands controlling external devices or encoding sensory information to be transmitted directly to the brain (see Figure 1).
The Potential Impact of BCIs:
There are numerous potential impacts of BCIs for persons who have suffered a severe brain injury. A BCI can allow someone who is paralyzed to control a limb again. BCIs may be used to stimulate regions of the brain to accelerate the brain’s reprogramming after a major injury. Some will be able to use a BCI to directly control an external device by sending signals from the brain to an external device. For individuals living with paralysis or severe communication barriers, BCIs offer the hope of regaining some abilities to interact with the world. In the future, devices may enable the blind to see via a direct connection between an electronic device and the brain. 1
Brain-computer interfaces have begun to enable individuals with traumatic injuries of the central nervous system to regain components of lost neurologic function, restore communication and mobility, and gain more independence. 2
Here are two short video clips about BCIs to help you better understand the technology and its implications. The first describes what these devices are and how they work [BCI overview]. The second demonstrates the benefit of such a device for a patient with ALS [BCI in ALS].
BCIs in Clinical Trials:
Several BCIs are being tested in clinical trials, each involving a few patients (see Table 1). Different devices and trials target different capabilities. One trial is focused on allowing a paralyzed patient to control a computer cursor by thought alone. Several trials are using BCIs to bypass a spinal cord injury and restore (partial) control over a limb. 3 Finally, a range of devices are being developed or trialed to accelerate brain recovery after injury. 4
Biologic Augmentation of BCI Benefits:
As discussed elsewhere, there is real hope that new medicines will be able to unlock the brain’s ability to regenerate after a devastating injury. Future medicines that stimulate the formation of new neurons, repair of damaged axons, or the enhanced plasticity of synaptic connections are all likely to promote functional recovery without the use of a brain-computer prosthetic device. These medicines may also be quite useful for recipients of BCIs. More specifically, preconditioning the brain through stimulating neurogenesis, providing autologous-derived neurons, or enhancing plasticity may amplify the benefits of (BCIs) for recipients with traumatic brain injuries. Even after the BCI is successfully implanted, the person will need protracted training and rehabilitation to learn how to use the device. Providing autologously derived neurons to replace lost tissue may be helpful for those whose injuries resulted in a substantial loss of viable brain tissue.
To be clear, the path towards useful BCIs will be challenging. Ethical considerations, technological limitations, and the need for personalized rehabilitation strategies remain pivotal areas requiring further exploration and refinement. Despite these hurdles, the trajectory of BCI technology is undeniably promising, driven by ongoing research, clinical trials, and the real promise of restoring meaningful ability to those who have suffered a devastating brain injury.
Table 1: Selected BCI Trials
| Company/Lad | Device | Essential Technology | Function Served | Reference/Link |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BrainGate Co. | BrainGate | Intracortical brain-computer interface | Enables individuals with paralysis to control assistive devices | BrainGate |
| Neuralink Corp. | Neuralink | High-bandwidth neural interface | Aims to facilitate direct communication between the brain and electronic devices | Neuralink |
| Synchron, Inc. | Stentrode™ | Minimally invasive stent-based electrode | Restores functional independence for severe paralysis patients by enabling them to control digital devices | Synchron |
| Duke University Center for Neuroengineering | Walk Again Project | Non-invasive BCI with exoskeleton | Restores walking ability in patients with severe spinal cord injuries | Walk Again Project |
| Blackrock Neurotech | MoveAgain BCI | Implantable BCI for motor control | Restores functional independence by enabling motor control of devices and potentially limbs | Blackrock Neurotech |
Figure 1: A BCI Example 5
References
- Hart, Robert. 2024. “Elon Musk Teases First Neuralink Products After Company Implants First Brain Chip In Human.”Forbes Magazine, January 30, 2024.https://www.forbes.com/sites/roberthart/2024/01/30/elon-musk-teases-first-neuralink-products-after-company-implants-first-brain-chip-in-human/.
- Pulse, Ieee. 2023. “The Future of Brain–computer Interfaces.” IEEE Pulse. January 25, 2023.https://www.embs.org/pulse/articles/the-future-of-brain-computer-interfaces/.
- Samejima, Soshi, Abed Khorasani, Vaishnavi Ranganathan, Jared Nakahara, Nicholas M. Tolley, Adrien Boissenin, Vahid Shalchyan, Mohammad Reza Daliri, Joshua R. Smith, and Chet T. Moritz. 2021. “Brain-Computer-Spinal Interface Restores Upper Limb Function After Spinal Cord Injury.”IEEE Transactions on Neural Systems and Rehabilitation Engineering: A Publication of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society 29 (July): 1233–42.
- Simon, Colin, David A. E. Bolton, Niamh C. Kennedy, Surjo R. Soekadar, and Kathy L. Ruddy. 2021. “Challenges and Opportunities for the Future of Brain-Computer Interface in Neurorehabilitation.”Frontiers in Neuroscience 15 (July): 699428.
- Vansteensel, Mariska J., Elmar G. M. Pels, Martin G. Bleichner, Mariana P. Branco, Timothy Denison, Zachary V. Freudenburg, Peter Gosselaar,et al.2016. “Fully Implanted Brain–Computer Interface in a Locked-In Patient with ALS.”The New England Journal of Medicine 375 (21): 2060–66.